Environmental Certifications
Below are two examples of reference standards for measuring environmental quality in the AEC sector.
PassivHaus Certification
This certification, under the PassivHaus-Institut founded in the late 1990s in Darmstadt, Germany, envisions a building that provides maximum thermal comfort with minimal energy demand.

Regarding the building’s location and orientation, the surrounding environment is taken into account in each case. For example, the placement of doors and windows is designed according to solar radiation and exposure to air currents. In houses outside urban areas, other factors such as proximity to an underground water flow may also be considered.
Another aspect analyzed in detail is the selection of materials and sealing techniques to prevent heat from flowing between the interior and exterior. For instance, materials that may generate thermal bridges or air leaks in conventionally unexpected areas, such as boxes housing blinds or pipes carrying wiring.
A passive building also emphasizes controlled ventilation systems that renew indoor air while recovering heat from the extracted air.
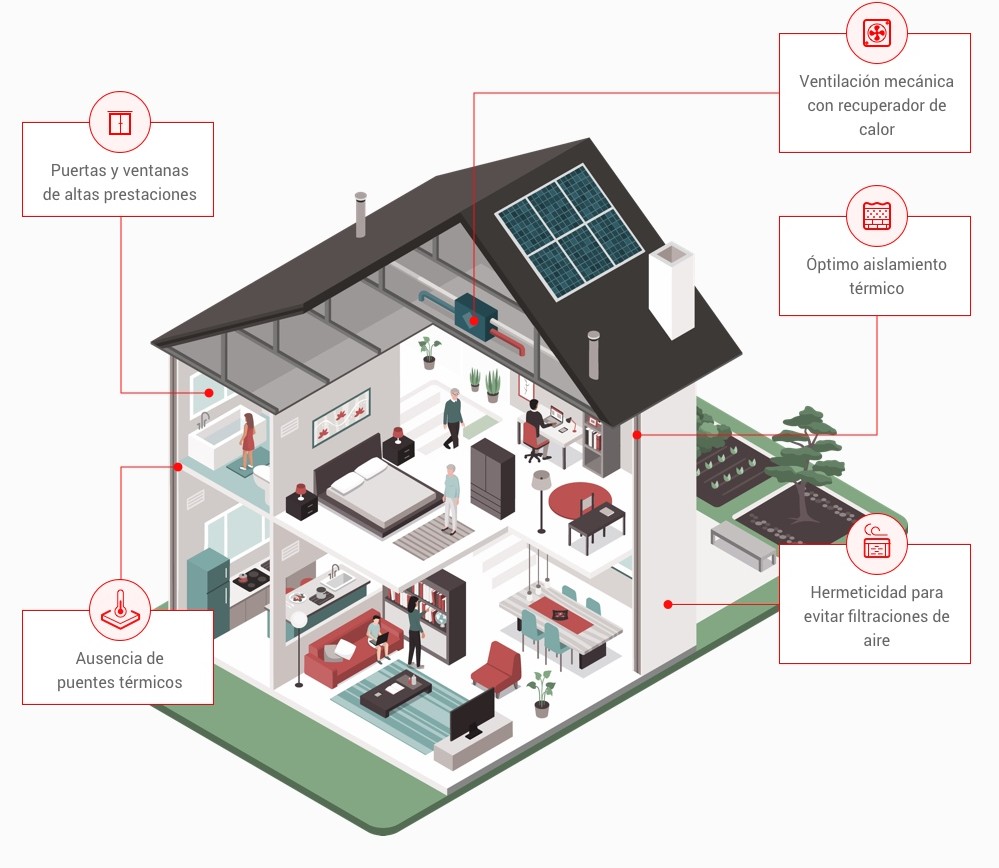
Key requirements include a heating and cooling energy demand below 15 kWh/m²/year, a total energy demand below 120 kWh/m²/year, and airtightness below 0.6 air changes/hour.

LEED Certification
Esta certificación nació en 1998 impulsada por el U.S. Green Building Council con el objetivo de estandarizar criterios de construcción sostenible para reducir el impacto ambiental de los edificios.

Para obtenerla, un proyecto debe cumplir prerrequisitos obligatorios y acumular puntos en categorías como energía, agua, materiales, calidad del aire interior, innovación y ubicación. Los requisitos incluyen eficiencia energética mínima, gestión responsable del agua, reducción de residuos, uso de materiales sostenibles y cumplimiento de normativas ambientales. La certificación se otorga en niveles (Certified, Silver, Gold, Platinum) según la puntuación total.
Strategies include optimizing passive design, improving thermal insulation, installing efficient HVAC systems, incorporating renewable energy, and implementing water-saving technologies. Materials with low environmental impact should be selected, recycling on-site promoted, indoor air quality improved, and sustainable mobility encouraged. Early integration of the design team is key.
